Level of competence in 2018
In 2018 KEINO conducted a survey, which was used to map the state of procurement competence for sustainable and innovative public procurement in Finland.
Respondents' background information
A total of 270 responses were received to the survey. Most of the respondents, a total of 84 %, worked in municipalities and joint municipal authorities (56 %) or the state (28 %). About 16 % of the respondents worked in parishes and others, such as independent educational institutions and companies owned by municipalities.
Almost half of the respondents, a total of 46 %, do procurement in addition to other activities, and the other half, a total of 42 %, full-time. 12 % of the respondents make procurement in other ways. Typically, they participate in the procurement process with their expertise or advice, but do not actually make procurements themselves.
Procurement competence and development needs
Respondents had to evaluate their procurement competenec and development needs on a scale: 1) I want to learn the basics, 2) I know something, I want to learn more, 3) I already know enough and 4) Not part of my job description/ tasks.
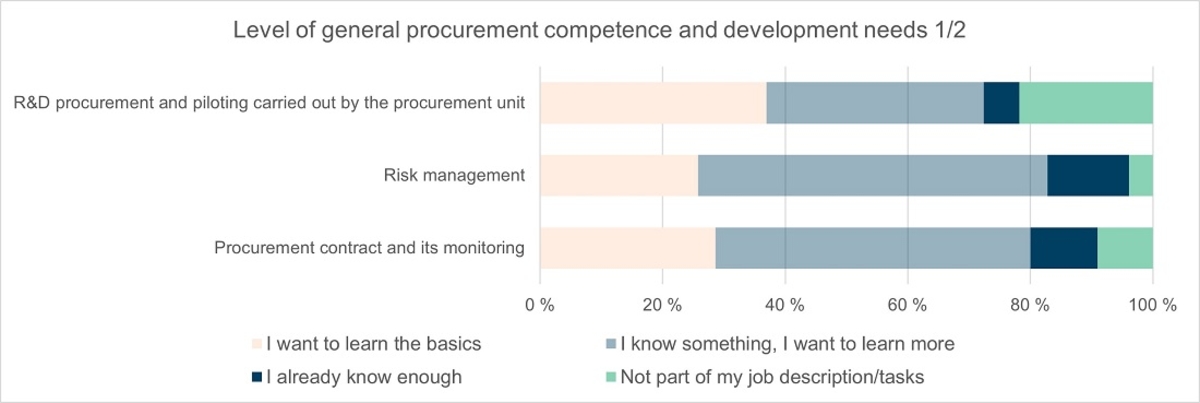
General procurement competence
The respondents were asked about the level of their procurement competence and development needs in the following themes: R&D procurements and piloting carried out by the procurement unit, risk management and the procurement contract and its monitoring. Basic skill development is most needed in R&D procurements and piloting carried out by procurement units.
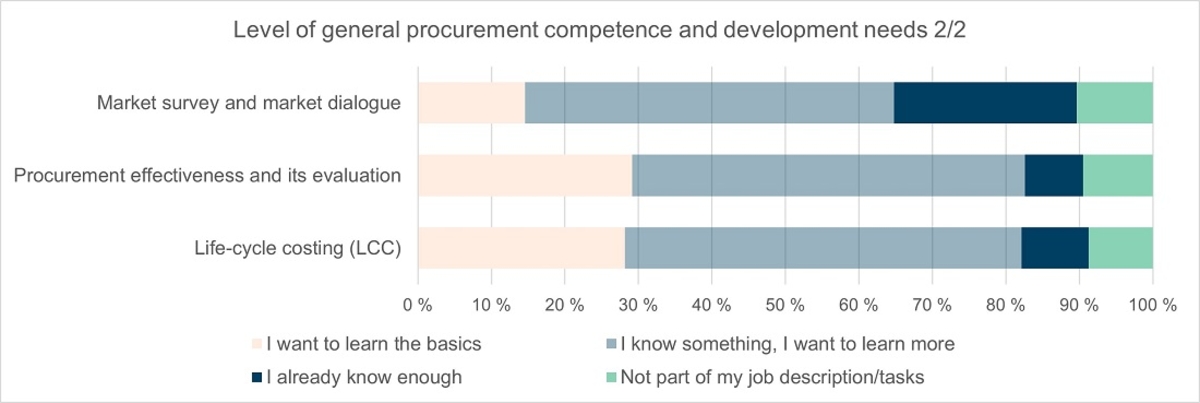
The level of competence was also asked about in the following themes: market survey and dialogue, the effectiveness of public procurement and its evaluation, and the life-cycle costing (LCC). Based on the answers, the respondents have the most expertise in implementing market surveys and dialogues (over 20 % answered that they already know enough).
In summary, with regard to general competence, it can be stated that for all themes of general competence there is a need for the development of both basic competence and in-depth competence.
Innovative procurements
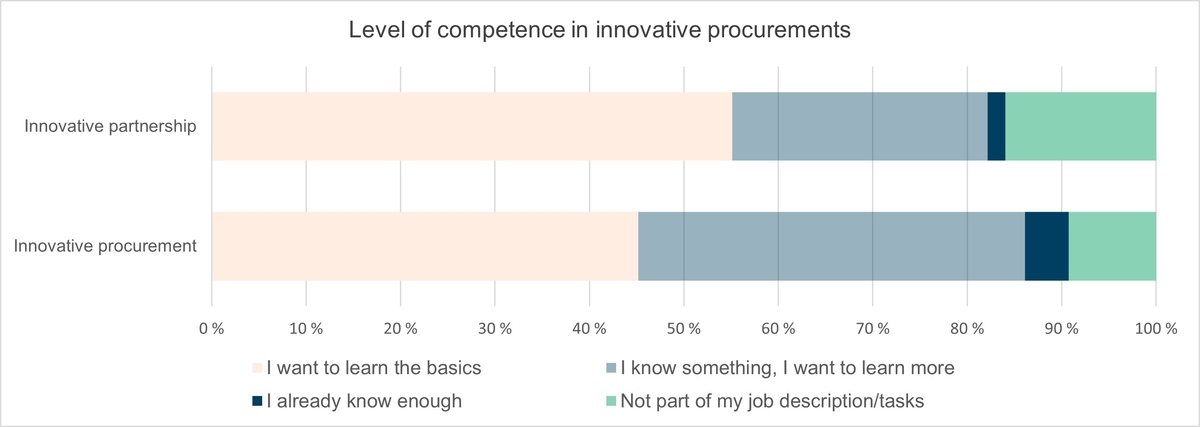
Regarding innovative procurements and especially the innovation partnership procedure, the respondents clearly had a need for the development of basic competence. In innovative procurements about 45 % of respondents wanted to learn the basics and in innovative partnership procedure about 55 %.
Environmental responsibility
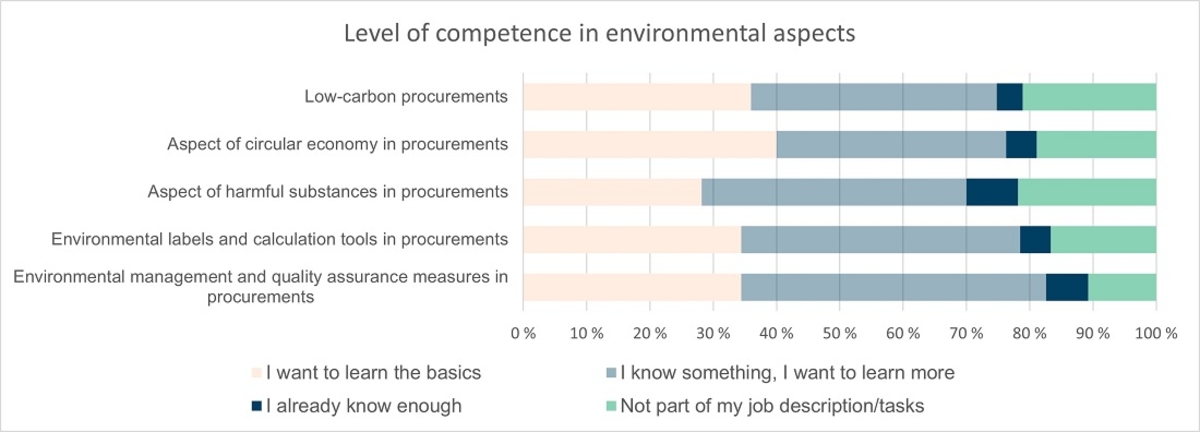
Regarding the different themes of environmental responsibility, there were no large variations in the need of competence development. Need for basic skills was between 28 % and 39 % in different themes.
Social responsibility
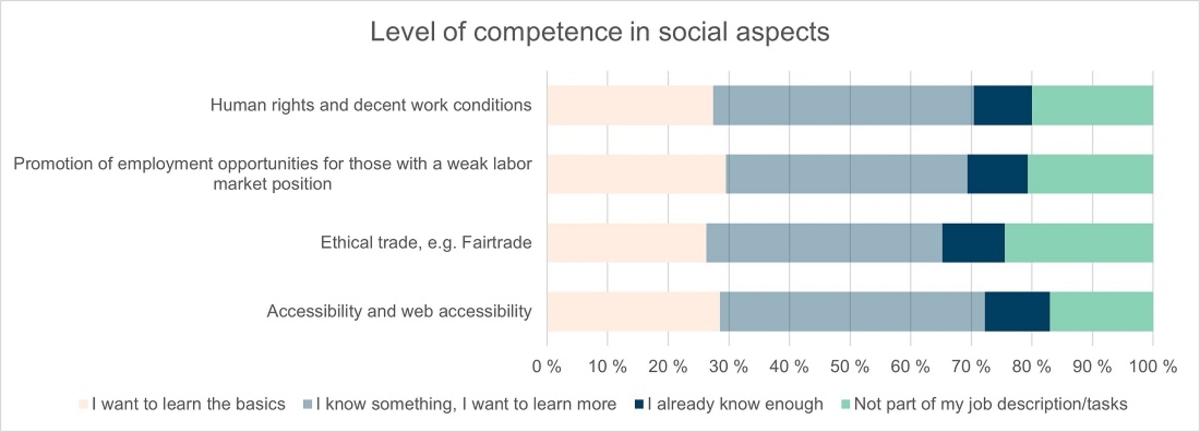
There were no big differences in the needs for competence development between the themes related to social responsibility. A surprising number of respondents answered that social responsibility is not part of their job description (about 20 % in every theme).
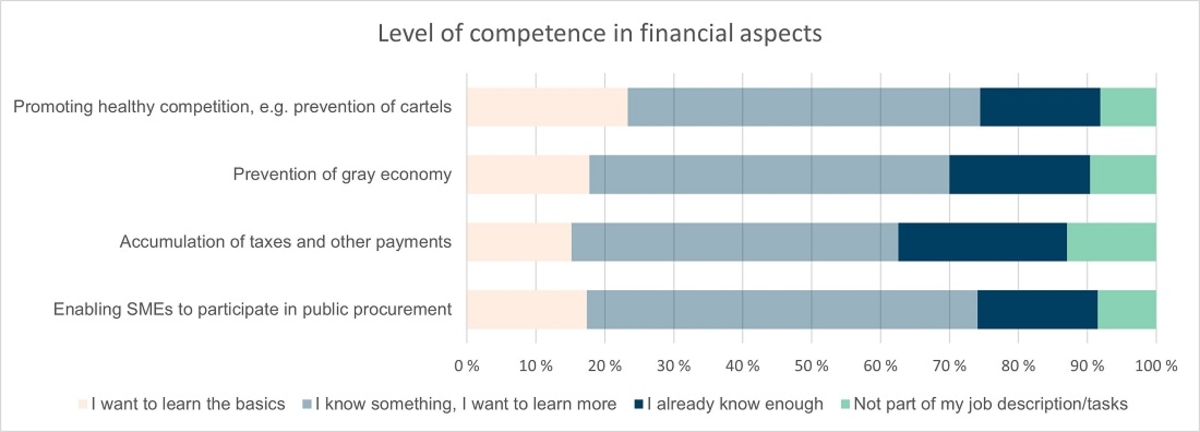
Financial responsibility
Regarding the themes of financial responsibility, the need to develop basic skills was slightly less than other themes. The differences between different themes are not significant. In the promotion of healthy competition, there is a little more need for competence development than in other themes.
Channels and tools for competence development
Respondents were asked about their wishes for channels and tools to develop their procurement expertise.
Webinars and seminars became the most popular methods of competence development. The respondents were also interested in face-to-face teaching and various materials enabling self-study, such as instructions, model documents and manuals. In addition, the respondents were also interested in guidance, sparring and peer learning with experts.
A follow-up survey was carried out in 2020.